In a world increasingly captivated by the pursuit of mindfulness, meditation has emerged as a beacon of solace and introspection, promising a refuge from the relentless pace of modern life. Its serene allure has transcended cultural and geographical boundaries, making its way into diverse therapeutic settings where it is embraced as a tool for healing and personal growth. Yet, as this ancient practice finds its place alongside conventional therapies, a pivotal question arises: should meditation be regulated in therapeutic settings? This article embarks on an exploration of this thought-provoking inquiry, delving into the potential benefits and pitfalls of regulation, and examining the delicate balance between preserving the integrity of meditation’s spiritual roots and ensuring its safe and effective integration into the realm of mental health care. Join us as we navigate the intricate tapestry of perspectives surrounding this timely debate, seeking clarity amidst the calm.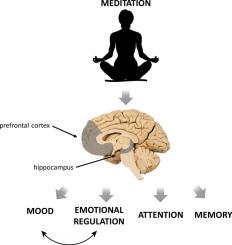
Balancing Serenity and Safety Exploring the Need for Regulation in Meditation Therapy
In the tranquil world of meditation therapy, the quest for peace often intersects with the critical need for regulatory oversight. While meditation has become a cornerstone in holistic health practices, its application in therapeutic settings raises important questions about safety and efficacy. The absence of standardized guidelines can lead to a myriad of challenges, including inconsistent practitioner qualifications and varied therapeutic outcomes. As meditation therapy continues to evolve, it’s essential to strike a balance that preserves the serenity of the practice while ensuring the safety of its participants.
- Ensuring Practitioner Competence: Without regulation, the qualifications of meditation therapists can vary significantly, potentially compromising the quality of care.
- Protecting Vulnerable Populations: Individuals with specific mental health conditions might require tailored approaches, emphasizing the need for regulated frameworks.
- Maintaining Therapeutic Integrity: Regulation can help maintain the integrity of meditation therapy by setting clear standards and expectations.
Ultimately, the discussion around regulation in meditation therapy is not about stifling the practice, but about enhancing it. By establishing guidelines that prioritize both the practitioner’s skills and the client’s well-being, we can create a harmonious environment where the therapeutic potential of meditation is fully realized, without compromising safety.

Understanding the Implications of Unregulated Meditation Practices in Clinical Environments
In clinical environments, meditation is often celebrated for its potential to reduce stress, enhance mental clarity, and foster emotional well-being. However, when these practices are unregulated, they may lead to unforeseen challenges. Without standardized guidelines, there is a risk of inconsistent outcomes, as practitioners might employ varying techniques with differing levels of effectiveness. Moreover, the lack of regulation can lead to ethical concerns, especially if individuals with limited training are facilitating sessions.
Consider the following implications of unregulated meditation practices:
- Safety Concerns: Without proper oversight, participants might engage in practices that could exacerbate mental health conditions.
- Quality Assurance: The absence of a standardized curriculum can result in a disparity of experiences, where the therapeutic benefits of meditation might not be fully realized.
- Professional Accountability: Regulation could ensure that practitioners are held to a set of ethical and professional standards, safeguarding client welfare.
While the integration of meditation in therapy is promising, a balanced approach is necessary to maximize its benefits while minimizing potential risks.

Crafting Guidelines for Effective and Safe Meditation Therapy Sessions
In therapeutic settings, the importance of crafting clear guidelines for meditation therapy cannot be overstated. These guidelines should prioritize both effectiveness and safety, ensuring that clients receive the full benefits of meditation while minimizing any potential risks. Practitioners should consider the following key elements:
- Client Assessment: Prior to starting meditation therapy, a thorough assessment of the client’s mental and physical health should be conducted. This helps in tailoring the meditation practices to suit individual needs.
- Qualified Instructors: Ensure that all meditation sessions are led by instructors with appropriate training and certification. This not only enhances the credibility of the therapy but also ensures the safety and well-being of the participants.
- Safe Environment: Create a tranquil and secure setting that fosters relaxation and concentration. Pay attention to aspects such as lighting, temperature, and sound to enhance the meditative experience.
- Emergency Protocols: Establish clear procedures for handling any adverse reactions or emergencies that may arise during a session. This includes having first-aid resources and contact information for medical professionals readily available.
By adhering to these guidelines, meditation therapy sessions can become a powerful tool for healing and personal growth, providing clients with a safe and structured pathway to inner peace and mindfulness.
Fostering Trust and Transparency through Standardized Meditation Protocols
Incorporating standardized meditation protocols in therapeutic settings is pivotal for cultivating trust and transparency among practitioners and clients. Standardization ensures that meditation practices are delivered consistently, which can enhance their credibility and effectiveness. This can be particularly important for individuals who may be skeptical about the benefits of meditation, as well as for those who have had negative experiences in the past.
- Consistency: Standardized protocols provide a consistent experience, reducing variability in outcomes.
- Accountability: Practitioners can be held accountable to specific guidelines, enhancing professional integrity.
- Safety: Clear guidelines help ensure that meditation practices are safe and appropriate for all participants.
- Efficacy: Uniform methods allow for better measurement of meditation’s therapeutic effects, contributing to more reliable research outcomes.
By adhering to standardized protocols, practitioners can also foster an environment of openness and clarity, where clients feel more comfortable expressing their experiences and concerns. This transparency not only builds trust but also encourages a collaborative approach to mental well-being, ultimately enhancing the therapeutic relationship.
Key Takeaways
As we draw the curtain on this exploration of meditation in therapeutic settings, the question of regulation remains a tapestry woven with diverse threads of thought. Like the gentle ripples on a tranquil pond, the implications of this debate extend far beyond the surface, inviting contemplation from practitioners, policymakers, and patients alike. Whether viewed as a sanctuary for personal healing or a frontier for structured intervention, meditation continues to hold a unique place in the realm of therapy. As we stand at this crossroads, the path forward is illuminated by the shared goal of enhancing well-being while honoring the rich, multifaceted nature of meditative practices. The dialogue is far from over; it is a living conversation that beckons us to listen, learn, and evolve together.
