In the tapestry of modern wellness practices, chakra meditation has emerged as a vibrant thread, weaving its way through yoga studios, mindfulness retreats, and digital platforms. Its colorful imagery of spinning wheels and energy centers captivates the imagination, promising balance and enlightenment to seekers worldwide. Yet, beneath this serene surface lies a complex narrative of cultural exchange, adaptation, and sometimes, appropriation. As we delve into the origins of chakra meditation, we find ourselves at the crossroads of ancient Hindu traditions and contemporary spiritual practices. This exploration invites us to ponder: Is chakra meditation a respectful homage to its roots, or has it been swept into the currents of cultural appropriation? Through an impartial lens, we will navigate this intricate landscape, seeking to understand the delicate balance between honoring a rich heritage and embracing a universal quest for inner peace.
Origins and Evolution of Chakra Meditation
Chakra meditation finds its roots deeply embedded in the spiritual traditions of ancient India, primarily within Hinduism and Buddhism. Originating from the Sanskrit word “chakra,” meaning “wheel” or “disk,” these energy centers were first referenced in the Vedas, the oldest sacred texts of Hinduism, dating back to 1500 BCE. The concept evolved through centuries, gaining intricate descriptions in later Upanishads and Tantric texts, where chakras were depicted as focal points of energy in the human body, aligned along the spine. In these early traditions, chakra meditation was not merely a practice of relaxation but a profound spiritual discipline aimed at achieving enlightenment and spiritual liberation.
As the practice journeyed beyond the borders of India, it was influenced by various cultures and spiritual ideologies. The New Age movement in the West adopted and adapted chakra meditation, often simplifying and reinterpreting its principles. This evolution led to a broader, more accessible understanding of chakras as tools for personal growth and healing. Today, chakra meditation is a synthesis of traditional Eastern philosophies and modern wellness practices, which sometimes raises questions about cultural appropriation. The practice now includes a variety of approaches such as:
- Guided Visualization: Using imagery to focus on each chakra’s color and energy.
- Sound Healing: Incorporating specific mantras or frequencies to balance chakras.
- Yoga Integration: Combining asanas (poses) to enhance chakra alignment.
While its essence remains spiritual and transformative, chakra meditation continues to evolve, reflecting a fusion of ancient wisdom and contemporary mindfulness.
Cultural Sensitivity and the Line Between Appreciation and Appropriation
When exploring the concept of chakra meditation, it’s essential to approach it with an understanding of the cultural sensitivity that surrounds practices rooted in Hinduism. Chakra meditation, originating from ancient Indian spiritual traditions, involves aligning the body’s energy centers, or chakras, to achieve balance and harmony. However, the global popularity of this practice has led to discussions about whether it is being appropriated or simply appreciated by those outside the Hindu culture.
- Appreciation: Involves a deep respect and understanding of the cultural significance of chakra meditation. This means engaging with the practice in a way that honors its origins and acknowledges the wisdom of the traditions from which it came.
- Appropriation: Occurs when chakra meditation is taken out of its cultural context, often stripped of its spiritual significance, and used solely for personal gain or commercial purposes. This can lead to a dilution of its profound meaning and an erasure of the cultural identity from which it stems.
Navigating this line requires mindfulness and a commitment to learning about the history and practices of Hinduism. By doing so, one can partake in chakra meditation in a way that respects its rich heritage while fostering a genuine appreciation for its transformative potential.
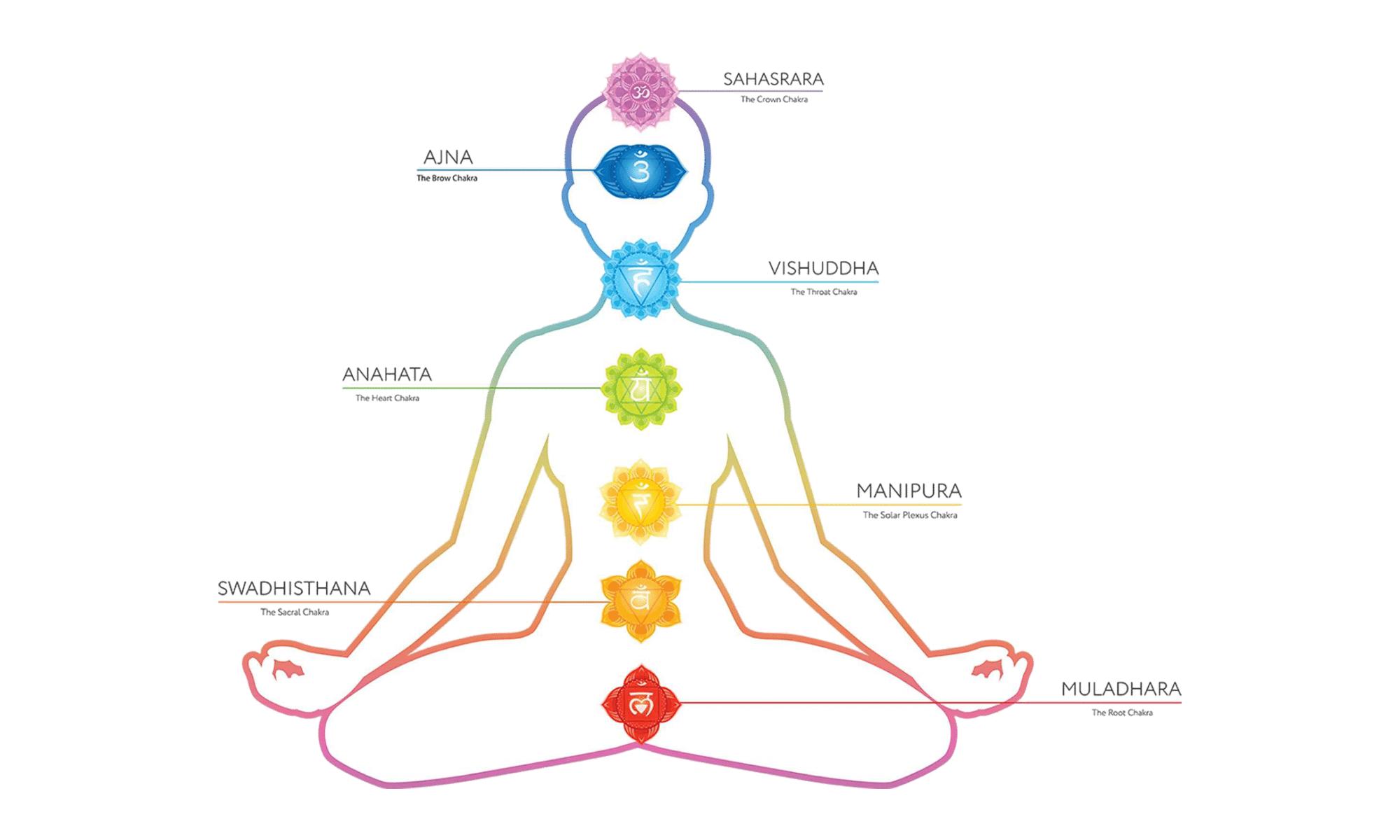
Exploring the Impact of Western Adaptation on Traditional Practices
The fusion of Eastern spiritual practices with Western wellness culture has sparked discussions on whether adaptations dilute or enrich traditional practices. Chakra meditation, rooted deeply in Hindu philosophy, offers an intriguing case study. While some practitioners argue that Western interpretations provide broader accessibility, others worry about the potential for misinterpretation and superficial engagement.
- Authenticity vs. Accessibility: The debate often centers around maintaining the authenticity of chakra meditation while making it accessible to a global audience. Western adaptations might emphasize the practice’s stress-relieving benefits, sometimes overlooking its spiritual and philosophical underpinnings.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Practitioners stress the importance of cultural sensitivity and respect. This involves recognizing the origins of chakra meditation and ensuring that its practice does not strip away the rich cultural and spiritual significance it holds in Hinduism.
- Educational Opportunities: With the rise of online platforms and workshops, there’s potential to educate Western audiences about the deeper aspects of chakra meditation, fostering a more informed and respectful approach.

Guidelines for Respectful Engagement with Chakra Meditation
Engaging with chakra meditation requires a thoughtful approach that honors its origins and respects its cultural significance. To ensure a respectful practice, consider these key guidelines:
- Educate Yourself: Dive deep into the historical and spiritual roots of chakra meditation. Understanding its connection to Hinduism can provide a more authentic experience.
- Acknowledge the Source: Recognize and appreciate the cultural heritage of chakra meditation. Giving credit to its origins fosters a deeper respect for the practice.
- Practice with Intention: Approach chakra meditation with a mindful attitude, focusing on personal growth and spiritual awareness rather than trend-following.
- Respect Cultural Symbols: Be cautious when using symbols, chants, or mantras that have specific cultural meanings. Misuse can lead to misinterpretation or disrespect.
By adhering to these principles, practitioners can engage in chakra meditation in a way that is both enriching and respectful, fostering a deeper connection to the practice and its cultural roots.
The Conclusion
In navigating the complex tapestry of cultural exchange, the practice of chakra meditation serves as a vivid illustration of both the beauty and the challenges inherent in our interconnected world. While its roots are deeply embedded in the spiritual traditions of Hinduism, its branches have extended across continents, transcending cultural and spiritual boundaries. As we reflect on its journey, we are reminded of the importance of honoring origins while embracing the evolution of ideas.
Ultimately, whether one approaches chakra meditation from a place of cultural reverence or as a modern practice for personal well-being, the key lies in mindfulness and respect. By fostering an awareness of its historical and spiritual context, practitioners can cultivate a practice that is not only enriching but also conscientious. As we close this exploration, let us carry forward a spirit of openness and understanding, recognizing that the path to enlightenment is as diverse and multifaceted as the world itself.
